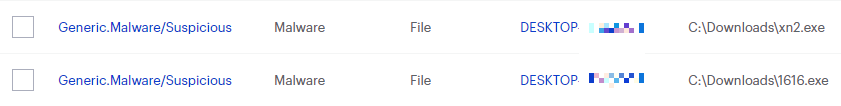
Trojan.Dropper
Short bio
Trojan.Dropper is Malwarebytes’ generic detection name for trojans that drop additional malware on an affected system.
Type and source of infection
Downloaders and droppers are helper programs for various types of malware such as Trojans and rootkits. Usually they are implemented as scripts (VB, batch) or small applications.They don’t carry any malicious activities by themselves, but instead open a way for attack by downloading/decompressing and installing the core malicious modules. To avoid detection, a dropper may also create noise around the malicious module by downloading/decompressing some harmless files.Downloaders often appear in non-persistent form. They install the malicious module and remove themselves automatically. In such a case, after a single deployment they are no longer a threat. If for some reason they haven’t removed themselves, they can be deleted manually.More dangerous variants are persistent. They copy themselves to some random, hidden file and create registry keys to run after the system is restarted, attempting to download the malicious modules again. In such cases, to get rid of the downloader it is necessary to find and remove the created keys and the hidden file.Downloaders and droppers emerged from the idea of malware files that were able to download additional modules (e.g. Agobot, released in 2002).An interesting example of a modern downloader is OnionDuke (discovered in 2014), carried by infected Tor nodes. It is a wrapper over legitimate software. When a user downloads software via an infected Tor proxy, OnionDuke packs the original file and adds a malicious stub to it. When the downloaded file is run, the stub first downloads malware and installs it on a computer, and then unpacks the legitimate file and removes itself in order to be unnoticed.Most of the time, the user gets infected by using some unauthenticated online resources. Infections are often consequences of activities like:
- Clicking malicious links or visiting shady websites
- Downloading unknown free programs
- Opening attachments sent with spam
- Plugging infected drives
- Using Infected proxy (like in case of OnionDuke)
They may also be installed without user interaction, carried by various exploit kits.
Protection
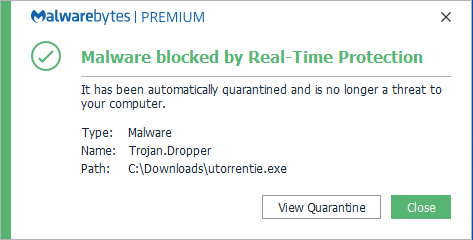
Malwarebytes blocks Trojan.Dropper
Home remediation
Malwarebytes can detect and remove Trojan.Dropper without further user interaction.
- Please download Malwarebytes to your desktop.
- Double-click MBSetup.exe and follow the prompts to install the program.
- When your Malwarebytes for Windows installation completes, the program opens to the Welcome to Malwarebytes screen.
- Click on the Get started button.
- Click Scan to start a Threat Scan.
- Click Quarantine to remove the found threats.
- Reboot the system if prompted to complete the removal process.
Business remediation
How to remove Trojan.Dropper with the Malwarebytes Nebula console
You can use the Malwarebytes Anti-Malware Nebula console to scan endpoints.

Nebula endpoint tasks menu
Choose the Scan + Quarantine option. Afterwards you can check the Detections pageto see which threats were found.
On the Quarantine pageyou can see which threats were quarantined and restore them if necessary.