Proxy (the authority to act for someone else) is a term that we use, when related to computers, to describe using a third party between the user and the internet.
Looking at the reasons to use a proxy will help us further on, when we look at the different kinds of proxies, and related methods. The most common reasons are:
- To hide your identity or location
- Speed, web proxies are commonly used to cache web pages from a web server
- Saving bandwidth for downloads, in cases where more users go through the same proxy to get the same files
- Usage logs, the proxy server keeps track of who goes where
- Security, the server scans the content for malware
- Other filters, in- and outbound
With this in mind we can have a look at the types of proxies.
A proxy server handles several clients. When these clients are unaware of each other and everyone is free to use the proxy server, we call these open proxies. Using an anonymous open proxy allows users to conceal their IP address while browsing the Web or using other Internet services. But here you still have to be careful, because there are levels of transparency in open proxies. Some proxies are transparent and will reveal your IP to the visited sites. One level up are anonymous proxies, that will not reveal your IP, but they do identify themselves as proxies and are therefore banned by some sites. Even stealthier are the distorting proxies that hide your IP and don’t reveal that they are proxies.
When the clients are organized in a closed network, for example in a company there are also several types in use:
- A proxy server that does not change the content is usually called a gateway or sometimes a tunneling proxy. A gateway server usually separates an enterprise network from the outside network and can be supported by a firewall, security software, administrative control and a caching service.
- A forward proxy handles the requests of the clients and forwards it, from the point of view of the internet service, it is the proxy server that issued the request, not the client. So when the server responds, it addresses its response to the proxy. This in turn forwards it to the client that made the request.
- A reverse proxy works more or less the other way around. It is easiest explained with the example of the employee out in the field requesting data from the company servers. The employee sends his request over the internet to the proxy server, which looks up the requested information on the company servers and sends it back to the employee (preferably encrypted).
Content filters
As listed earlier, content filters are one of the reasons that proxies are used. The common use of a corporate gateway is adding security and sometimes caching sites that are frequently visited by several clients. You can imagine the server having filters and on-the-fly scanners to take away the need for extra security software on all the client computers.
On the other hand an open proxy can just as easy be used by one of the clients to circumvent the filters that are active on a company gateway. By connecting the clients computer to a proxy the gateway cannot “see” that the client is visiting prohibited sites. From the gateway point of view the client is connected to an IP that is allowed. In reality that IP is the proxy the client is using to surf the internet.
If you are travelling or living in a country with strict censorship rules or wish to use a proxy often for other reasons, then it would be advisable to install proxy server software or a VPN (virtual private network) on your computer. A VPN protects your data and identity over the Internet. Various protocols are used to create an encrypted tunnel that transports data securely. VPNs are commonly used when using public WiFi hotspots, common in airports and hotels, these are potential leaks because they offer streams of visible data waiting to be mined. Using a VPN keeps your information secure. And they offer you the option to access websites only available to users from a certain country.
Finding suitable, reliable and fast proxies everyday can be a hassle and proxy server software or a VPN can take care of that for you. Consider for example CyberGhost, user friendly and works like a charm. Originally VPNs were designed to link together LANs and workstations outside the main LAN belonging to one company.
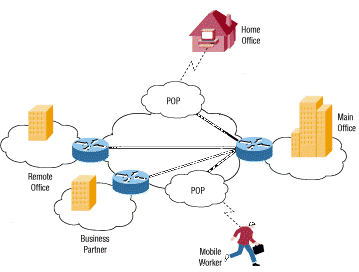
So basically this type of VPN uses the internet to connect several computers and closed networks, but it adds security to the connections. You can find more technical details on the Cisco site.
But “It is very naive to think that by paying a subscription fee to a VPN service you are free to break the law without any consequences.” This statement came from HideMyAss, after they provided logs about the lulzsec hacking group to the FBI. And it would be wise to heed that warning. If you intend to do something illegal, you’ll have to go through more trouble than simply use a third party VPN service, free or paid.
And then there is TOR.
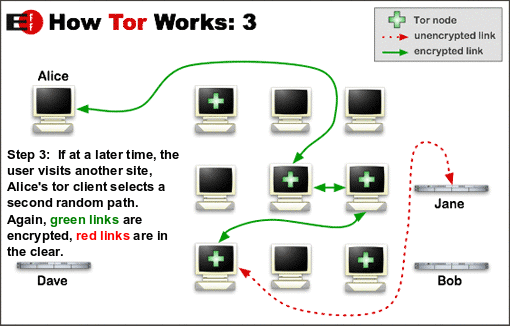
TOR is a service that depends on the “strength in numbers” principle. It is like jumping from a bus into a taxi to the train-station. Shaking of pursuers (traffic analysis) by using random hops. The intermediate stations are unaware of the original sender and the final destination. After mapping out the route when the original request is made, the circuit is extended one hop at a time, and each relay along the way knows only which relay gave it data and which relay it is giving data to. No individual relay ever knows the complete path that a data packet has taken. And the content of the traffic is encrypted. For efficiency, the Tor software uses the same circuit for connections that happen within the same ten minutes or so. Later requests are given a new circuit, to keep people from linking your earlier actions to the new ones.
A great guide on how to install TOR can be found in an earlier blogpost by Adam
Whichever method you decide to use when the need is there, remember that with the complexity of the method, the price you pay is in the speed of your connection.
Summary: this article describes the reasons for using proxies and the different types. It also discusses some more advanced techniques for hiding your identity or location online.
Sources:
http://blog.hidemyass.com/2011/09/23/lulzsec-fiasco/
http://www.jscape.com/blog/bid/87783/Forward-Proxy-vs-Reverse-Proxy