Last week, we touched on several online threats that were in the wild:
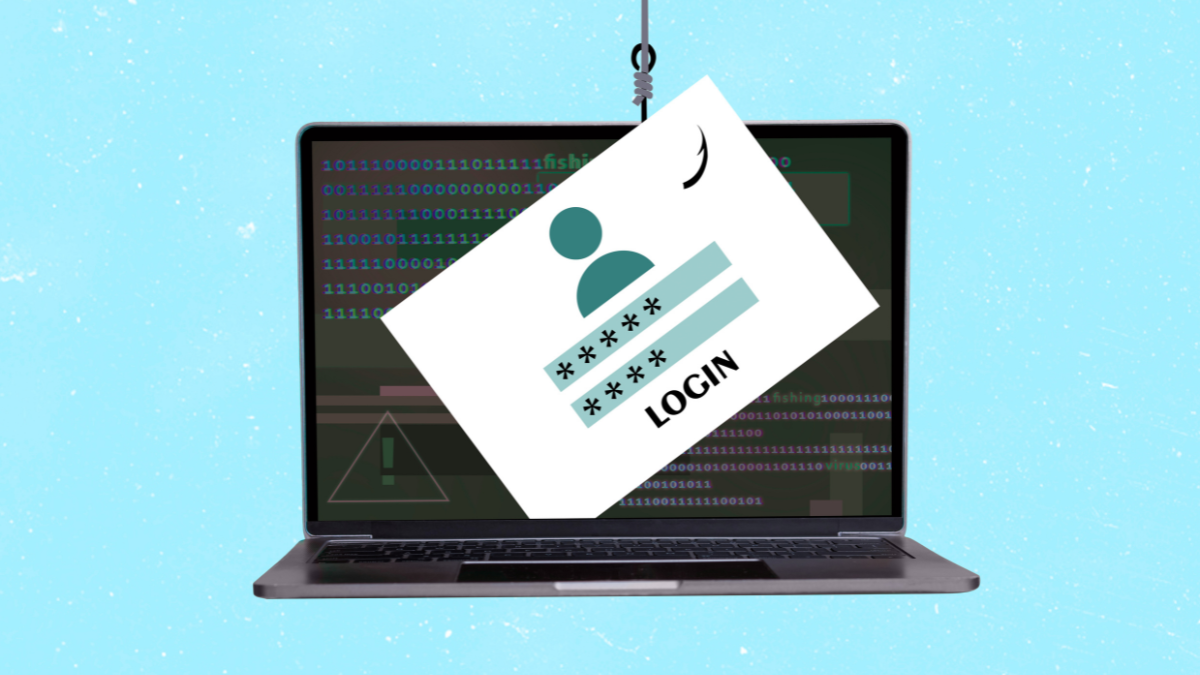
- Safe Browsing Scam: From Amazon to Rackspace. Senior security researcher Jérôme Segura observed that some tech support actors moved from using Amazon as their service-of-choice when it comes to serving their tech support pages to using Rackspace, another cloud provider.
- WebSearcher PUP applies Proxy Lockdown. Security researcher Pieter Arntz discussed WebSearcher, an adware that comes bundled with a variety of applications, including video players and codexes. It was found to use a proxy to insert advertisements. Unlike other simple adware, this one modifies affected browsers by making changes to their proxy settings, in turn locking out users from modifying them.
Notable news stories and security related happenings:
- Phish and chips: Retailers Face New Liability for Fraud Committed with New Chip Credit Cards. “While the technology giving rise to chip cards is new, the cards are already causing a number of security concerns. The FTC has recently issued warnings about phishing attacks asking people to click on a link and enter personal information in order to receive a new chip card. Further, there are concerns that the cards will be intercepted in the mail while on the way to consumers.” (Source: Advisen Cyber FPN)
- Microsoft Now Alerting Users To State-Sponsored Attacks. “The announcement comes following a Dec. 30 Reuters report that sourced former Microsoft employees and claimed the company did not tell users that Chinese authorities had hacked over a thousand Hotmail accounts years ago.” (Source: Information Week)
- Employees Take Sensitive Company Data When They Leave the Job: Survey. “A recent survey from secure communications solutions provider Biscom, measuring the behaviors of entry level to senior level employees in eight different industries, reveals that when employees leave their job, they frequently take and/or share sensitive company data, and businesses are not prepared to combat this.” (Source: Legal Tech News)
- As Internet Gets Faster, Volume of DDoS Attacks Grows, Akamai Reports. “From a security perspective, Akamai reported that it defended against 1,510 distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks in the quarter, which is a 180 percent year-over-year increase. While the number of DDoS attacks rose, the top DDoS attack in the quarter came in at 149G bps, a decline from the 250G-bps peak reported in the second quarter.” (Source: eWeek)
- Android Malware Poses As Google App To Ditch Security Apps. “The malware has been named Android.Spywaller and it is being deemed as a unique threat because during the infection it searches for a popular Chinese security app Qihoo 360.” (Source: HackRead)
- Users No Longer Need to Jailbreak Apple iOS To Load Rogue Apps. “Security practitioners who’ve counted on the protection of Apple App Store’s walled garden approach now have something new to worry about: rogue app marketplaces are now using stolen enterprise certificates to allow users with even non-jailbroken iPhones and iPads to download applications through unapproved channels.” (Source: Dark Reading)
- The Splinternet: A New Era of Censorship, Surveillance, and Cyberwarfare. “Individual countries around the world want to lay down their own rules about the data that is released to their citizens. As these states slowly carve up the internet for their own purposes, it’s not just the universal aspects of the web that are in jeopardy— some fear the growing aggressiveness of individual states could lead to a potential cyberwar.” (Source: The Take Away)
- Adobe Fixes Flash Zero-Day Bug Discovered by Huawei. “Adobe has just released new Flash Player versions 20.0.0.267 and 18.0.0.324 to fix a critical security issue used in the wild by attackers. Additionally, version 11.2.202.559 has been released for Linux users.” (Source: Softpedia)
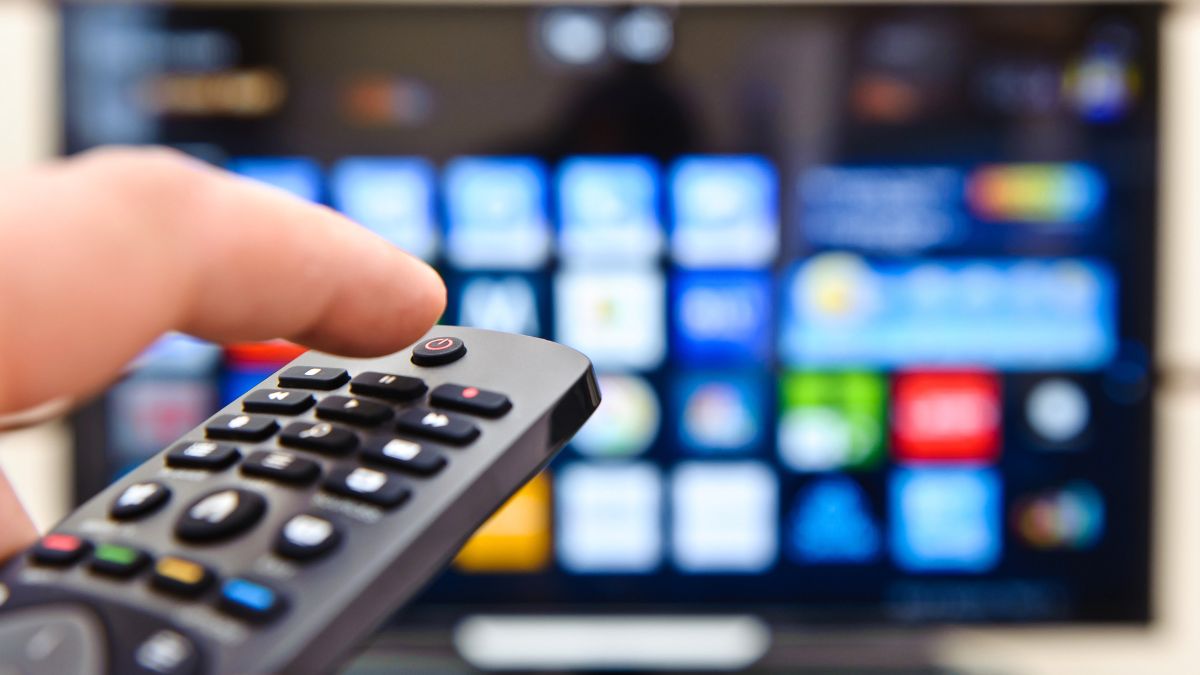
- The Next Wave of Cybercrime will Come Through Your Smart TV. “Smart TVs aren’t just consumer items, either, as the devices are often used in corporate board rooms. Sales of smart TVs are expected to grow more than 20 percent per year through 2019, according to Research and Markets.” (Source: CSO Online)
- Common Payment Processing Protocols Found to be Full of Flaws. “Much research has been done into the chips found on credit cards and the readers and number pads used with these cards, but Nohl decided to take a different approach, looking instead at the communications protocols used by those card readers. There are two that are significant; the first, ZVT, is used between point of sale systems and the card readers. The second, Poseidon, is used between the card reader and the merchant’s bank. Nohl found that both had important flaws.” (Source: Ars Technica)
- 15 Cybersecurity Lessons We Should Have Learned From 2015, But Probably Didn’t. “As is the case every year in the cybersecurity field, 2015 was full of lessons to be learned. Some brand-new, others that it’s absurd we haven’t learned from yet.” (Source: Dark Reading)
Safe surfing, everyone!
The Malwarebytes Labs Team