Short bio
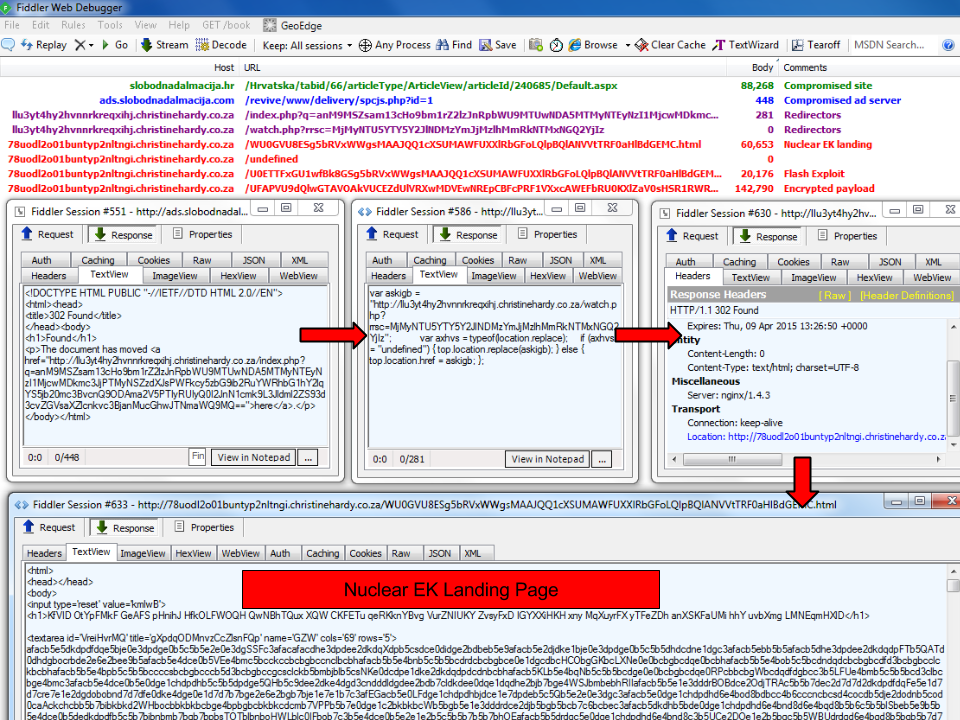
Exploit kits are efficient and effective tools for cybercriminals to distribute malware. Exploit kits include exploits for multiple vulnerabilities within a single malicious webpage. Cybercriminals are able to check for vulnerabilities in operating systems, web browsers, and browser plugins so as to launch an exploit specific to the identified vulnerability. And this is how Nuclear operates.
History
Nuclear has been used in many campaigns, such as the AskMen compromise, and the APT group behind Operation Windigo, which was also associated with Nuclear and Glupteba. Nuclear has a vast selection of attacks to choose from, including Flash, Silverlight, PDF, and Internet Explorer exploits. Cybercriminals are constantly improving Nuclear trying to stay one step ahead of security companies.
Common infection method
Compromised ad servers are used to re-direct victims to Nuclear exploit kits. Drive-by downloads are also a common infection method. Code injection is used for re-directing victims to Nuclear EK landing page. The goal of EKs are to exploit a vulnerability in the victim system, via unpatched or zero-day vulnerabilities.
Associated families
Exploit kits/packs and ransomware.
Remediation
Malwarebytes Anti-Exploit stops Nuclear EK while Malwarebytes Anti-Malware already detects known dropped binaries, such as Andromeda/Gamarue malware. Keep your system patched and keep your applications updated.
Aftermath
Successful exploitation of a victim system varies but can lead to an encrypted executable download. The binary is decrypted and begins beaconing immediately, which can lead to CryptoWall.
Avoidance
It is best to practice good security by keeping systems patched and programs updated. Ensure you keep your browser and plugins up-to-date. Furthermore, ensure you have anti-virus, anti-exploit, anti-malware protection. For even more protection, it is good to have a dedicated firewall.
Screenshots