What you need to know
- Digital citizenship is about using technology wisely. It incorporates thinking critically and treating others with respect online.
- It’s not just about protecting yourself as it also helps to create a better online environment for everyone.
- Every click or comment adds to your digital footprint. Being mindful helps protect your privacy and reputation and is the right thing to do for your future.
- Showing empathy and kindness online makes a difference in reducing bullying and misinformation.
- Digital citizenship is a lifelong skill that matters at any age.
- Simple and tiny habits can make the internet a safer and more positive place.
Definition: what is digital citizenship?
Ever noticed how some online communities feel less safe or poorly moderated? This is partially down to the lack of digital citizenship and “netiquette” shown in those places.
Digital citizenship describes how we all use the internet responsibly and ethically. It defines how we interact in online spaces and the impact of our behavior on others.
How do experts define digital citizenship?
Different people have slightly different definitions but digital citizenship always relates closely to the ethical use of technology in daily life. We share the internet in many ways and the concept of citizenship is about how people talk and engage in online communities.
Respect and critical thinking are absolutely key as well as an understanding of some of the significant dangers of the internet. There are social and moral skills that make digital spaces healthier for everyone.
Netiquette is another term you’ll probably see used in similar contexts, which describes the norms of polite and responsible communication online.
What makes someone a digital citizen?
Anyone who uses the internet is a digital citizen in some respect. A good digital citizen is sensible and empathetic online. It is always best practice for a citizen to do things like thinking before posting and verifying information before sharing it with friends on Instagram or Facebook.
Dr. Mike Ribble has spread the term and become a key name in this particular area. He published the Themes of Digital Citizenship (https://www.digitalcitizenship.net/nine-elements.html).
These are: digital access, digital commerce, digital communication, digital literacy, digital etiquette, digital law, digital rights and responsibilities, digital health and digital wellness, and digital security.
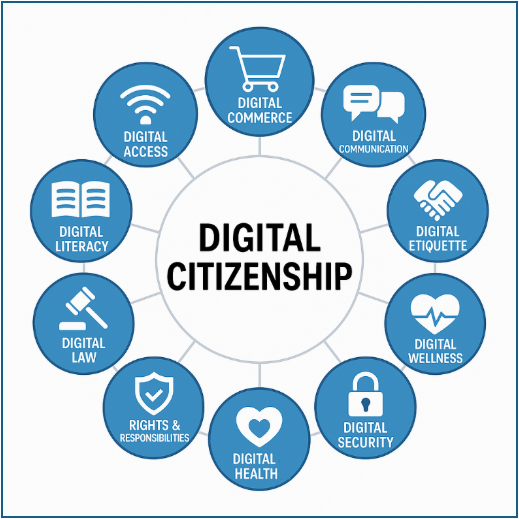
Ribble also set up the S3 Framework (Safe, Savvy, and Social) to try and protect people and give them more knowledge online.
Why does digital citizenship matter today?
Why is digital citizenship important? Connections and choices you make on your phone or computer can affect far more than just your screen.
How does it protect your safety and privacy?
Digital citizenship starts with protecting yourself by using classic safety precautions. You will probably already know the importance of setting strong passwords and thinking twice before sharing personal details. These small habits form the foundation of good cybersecurity.
Scams like phishing emails that look real or fake login pages are prominent but if you know the warning signs then you’re far less likely to fall victim. Using trusted security tools such as VPNs or strong antivirus suites like Malwarebytes adds another layer of defense and protects devices. They help to keep your information private and block malicious sites.
Every action you take online either strengthens or weakens your digital security. Digital citizenship helps you stay aware of those risks before they turn into problems.
How does it build healthier online communities?
Cyberbullying and misinformation are commonplace online.
Healthy online communities rely on people who pause before reacting and choose their words with care. Good digital citizens know when to disengage and how to report harmful behavior.
Best practice in digital citizenship also means knowing when and how to act when there is a problem. This often means reporting unhealthy or threatening behaviors such as abuse or scams.
How does it impact your future?
Nearly all web users have a digital footprint that can influence how others see them. That includes employers and universities that may pass on applicants either because of an honest mistake someone made years ago, a quick repost of material that later turned out to be misinformation, or because of images that were posted without their consent. .
Good digital citizenship helps you build a reputation for honesty and avoid unwanted attention later on.
Fake news is a problem for everyone in the modern age and we need to be conscious of it whenever we go online (especially with AI’s input). Digital citizens also play a key role in fighting misinformation and helping to hold people accountable so that the future can be safer and people can be better informed.
What are the core principles of digital citizenship?
Digital citizenship can be boiled down to three simple principles that apply to all areas of online activity. ul, but being smart and never sharing details unless you are certain it is safe are still the best protections.
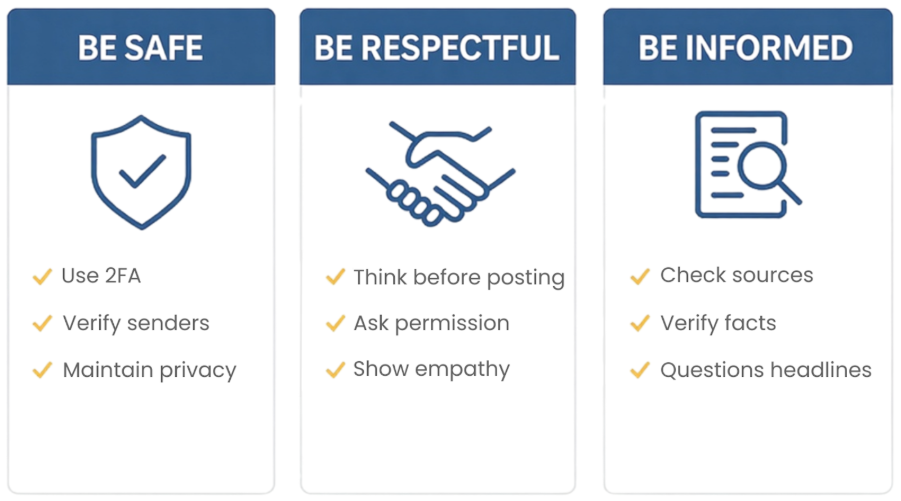
1: Be safe
Safety basics include taking control of your personal information and staying alert to online threats. It is recommended to turn on two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible and check your privacy settings on social media to control who can see your posts. Only the people you want to see your posts should. Basic precautions like these can form the basis of a strong online presence and your own personal privacy.
Try to stay on top of trends in areas like phishing scams so you have a good idea when fake emails or messages appear. They’ll claim to be from official sources or even desperate friends who say they’re being scammed or are stuck in an airport needing some financial help. Don’t click suspicious links or share private details without verifying the sender.
Being safe online means managing your personal information wisely and staying alert to threats. Safety isn’t a single action, but a daily mindset that protects your privacy and builds trust across digital spaces.
2: Be respectful
There aren’t too many complex rules to use as etiquette and respect online works just like it does offline. It’s about empathy and accountability.
Good netiquette means choosing your words carefully and remembering that there’s a real person behind every screen. Some people forget that there’s a real person on the other side of the screen, which can make online conversations feel less personal.
Pause and reread what you’ve written before posting it online. Would you say it to someone face-to-face? Always ask permission before sharing someone else’s photo or story. Consent makes up a huge part of respect.
3: Be informed
The modern web user needs to understand how information spreads online and how easily it can be manipulated by others. Algorithms and filter bubbles often show us content that fits our interests or beliefs and reinforces our biases. This makes it harder to see other perspectives or spot misinformation when it is presented online. It is also a form of online confirmation bias.
Get into the habit of verifying what you read before sharing it. Check the source, date, and credibility, then compare it with information from trustworthy outlets. Fact-checking tools and educational sites can help you stay grounded. Many people only learn to analyze and question sources in high school or college, but it’s a tip that can guide you for the rest of your life.
Think before you share. One click can amplify false information but it can also spread truth. What is a digital citizen? It is the person making the decisions on what to share. The world is a better place when those citizens are responsible.
What are the biggest challenges to good digital citizenship?
Society does face some inevitable challenges in the quest to create a fairer and safer digital world.
What is the digital divide?
This is the term we use to describe the gap between people who have reliable access to technology and those who don’t.
Reliable internet connections and access to basic online resources sadly aren’t available in all parts of the world. This divide affects education and even participation in areas of modern life and deprives some people of the basic benefits of a connected world.
Students without stable internet connections fall behind in online learning while adults without digital tools may miss out on job applications or education.
Bridging this divide means ensuring equal opportunity to learn and connect in the digital age.
Society benefits from the connections of the internet and the way it facilitates things like working from home and applying for jobs or even healthcare information. Closing the gap builds a stronger workforce. It also makes online spaces more inclusive for everyone.
Why is misinformation such a threat?
Misinformation spreads fast. We see this especially when it plays on fear or emotion. Fake news and conspiracy content can be very convincing and indistinguishable from something that is real. This type of content is often designed to provoke quick reactions before anyone checks the facts or even if it is legitimate.
The best defense is awareness. Before you share a post or headline:
- Check the URL. Small spelling changes often reveal fake websites.
- Use fact-checking tools like Snopes or BBC Verify.
- Pause before sharing emotionally charged content.
- Being a responsible digital citizen means recognizing that not every viral story deserves your trust.
How can we reduce online harms like cyberbullying?
Cyberbullying and doxxing are some of the most damaging behaviors that are unfortunately common online. They can destroy reputations and have a terrible impact on victims’ mental health. This is a particular problem among young users who may be more easily led. Good digital citizenship means refusing to participate in harassment and taking steps to protect yourself and others.
If you’re being targeted:
- Don’t respond. Avoid giving bullies the reaction they want.
- Take screenshots as evidence in case they are required.
- Report or block the user on the platform.
- Reach out to someone you trust or a mental health professional if it’s affecting you emotionally.
Everyone can help by reporting abuse early and supporting people who are targeted. Consistent action and accountability leave less room for harm to grow.
How can you practice good digital citizenship every day?
This isn’t about perfection. A little awareness each day can make a big difference in your safety and overall online experience and lead to better habits.
3 simple habits that will make you a safer digital citizen:
- Turn on two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible.
- Update your devices regularly to patch security flaws.
- Avoid clicking suspicious links or attachments, even if they look familiar.
Regularly check your app permissions and think carefully about what you share publicly. Limit personal details like location tags or financial information.
These small routines add up. A few seconds spent verifying a link or tightening privacy settings can prevent loss and damage control after a security breach.
How can families and workplaces build digital citizenship together?
Digital citizenship works best when everyone shares responsibility. Parents and teachers play a role in setting expectations and behavior for the next generations and this includes both offline and online etiquette.
It can start at home and families can create open conversations about online behavior instead of relying on strict rules that confuse children. Open conversations help young people to understand the reasons they need to be safe and secure online.
Schools and colleges can include digital citizenship lessons alongside academic subjects and give young people more knowledge to use against threats. It is likely that young people will be using the internet for schoolwork so they should be taught how to do so safely.
Workplaces can also play a part and can also promote digital citizenship by setting clear technology use policies. They may also offer online security training and set clear expectations for team communication. Leaders who model good habits help build trust across any organization.
How can you teach kids to be good digital citizens?
Teaching good citizenship principles can help kids become more confident and responsible online. Kids naturally explore the internet. This means that guidance should start early and grow as they do.
When should kids start learning about it?
Teaching should start as soon as a child begins using a device and can understand the basics of the internet. Simple lessons like being kind online and keeping personal information private can help not to overwhelm young people.
Teaching online respect and safety early helps kids build healthy digital instincts that last a lifetime. Many parents and teachers make learning interactive by using games or examples. These keep children engaged and show what is expected for safe online spaces.
What should parents focus on first?
Start with the essentials:
- Don’t share personal information like addresses or school names.
- Create strong passwords for every account.
- Always ask an adult for help if something online feels confusing or wrong.
Children learn best by example. When parents model respectful communication and empathy online, kids tend to follow. Setting up family tech rules can help maintain balance. This could mean something like a simple rule about no screens at the dinner table.
Parents have tools available. They can also enable safe browsing settings along with other parental controls. The goal isn’t to control every click. It is to build trust and confidence so kids grow into responsible digital citizens. Open conversation is absolutely crucial to this.
How can students practice digital citizenship in school?
Young people need to understand using technology to learn and communicate responsibly. Students who understand how their actions affect others can develop skills that are of use far beyond the classroom.
What does digital citizenship look like for students?
Good digital citizenship for students means showing integrity and awareness in digital interactions. That includes how they collaborate with other students on shared projects and present their work online. Discussions between students should always be mutually respectful (this is a basic of the classroom) and this includes online discussions.
Students should:
- Respect copyright by citing sources properly and avoiding plagiarism.
- Engage respectfully in all digital spaces. This includes Google Classroom or school forums.
- Think long-term about their digital footprint. Colleges and employers often look at online behavior.
How can schools help students become responsible digital citizens?
Teachers and schools play a key role in shaping digital habits early on. They can make media literacy and responsible communication a normal part of everyday learning.
Clear classroom guidelines help. Many schools have rules for device use as well as respectful posting in forums. There are also often discussions about what’s appropriate to share on school social media accounts. Schools that put the focus on conversation rather than punishment help students understand why responsible behavior matters.
How can education and awareness improve digital citizenship?
Technology changes faster than most curriculums and it can be hard to keep up. Both kids and adults need regular updates to keep pace with the online world.
Why should schools teach digital citizenship early?
Teaching digital citizenship early helps students become safer and more confident online. Programs like Common Sense Education and other K–12 digital literacy curriculums teach key skills like:
- Recognizing scams and suspicious content
- Managing privacy settings
- Communicating with empathy and kindness
- Thinking critically about information they encounter
These lessons prevent many online harms before they begin. Problems like cyberbullying and misinformation are huge for every generation. It is important to arm people with information. This includes young people at schools. Many schools teach digital citizenship for kids.
How can adults keep learning and adapting?
Digital citizenship doesn’t end after school. Adults should make an effort to stay informed. This can happen through workshops or community training that cover privacy and technology use.
Organizations like the OECD and FTC offer consumer education and free resources to help people stay aware of evolving digital risks. Technology is always moving forward, from new social platforms to artificial intelligence. These changes shape how online threats appear and evolve. The key is to stay curious and adaptable. Continuous learning keeps you safe and empowered online.
How can you turn digital citizenship into digital leadership?
Digital citizenship only hits its full potential when people use it to lead and educate others. This helps the positive behaviors to survive and negative ones to dwindle.
What does being a “digital leader” mean?
Digital leaders use their voices to share knowledge and stand up against misinformation or harmful behavior.
Leading might mean mentoring younger users or advocating for ethical tech use across the internet. True digital leadership turns online safety into community empowerment. Digital leaders report harmful content and help others stay informed. The internet should be a positive, informative space for everyone. That only happens when people lead by example and push back against misinformation.